本文
【NINS】自然科学研究機構、名古屋大学、九州大学による、日本初のプラズマバイオロジー研究共同体「プラズマバイオコンソーシアム」を発足 ~低温大気圧プラズマの生命科学・医療への応用を目指して~
Updated : July 23, 2018
Contents
In collaboration with Nagoya University and Kyushu University, Inter-university Research Institute Corporation National Institutes of Natural Sciences has launched the Plasma Bio Consortium, Japan's first plasma biology research community. Nagoya University and Kyushu University use the "low temperature atmospheric pressure plasma" technology to lead the world with outstanding achievements in selective cancer death, regenerative medicine such as wounds, growth promotion of plants, and production of functional plants. It has been done. In the consortium, the Natural Science Organization will take the lead in promoting joint research, pioneering "new plasma life sciences", and create an innovative mechanism to create future medical and agricultural new technologies from Japan. It also aims to become.
For example, as typified by water, it is known that a substance changes its state from solid to liquid to gas by raising its temperature. Then, by raising the temperature further from the gas or applying a voltage, ionization occurs, and the substance changes to a state in which neutral molecules, electrons, etc. coexist. This state is called plasma. Auroras and lightning, etc., found in nature are representative of plasma, and technological applications of this are fluorescent lamps and plasma TVs.
Plasma has high particle temperature plasma (high temperature plasma) and low temperature plasma. High-temperature plasma is used in the fusion technology developed by National Institute for Fusion Science, which aims to generate energy equivalent to the sun on the ground. On the other hand, low-temperature plasma has attracted attention in the industrial world due to its versatility, ease of handling, and inexpensive equipment, and is used for semiconductor technology, sterilization and disinfection.
In recent years, research on the application of low-temperature plasma to the fields of life sciences and medicine has been advanced worldwide, and in Japan it is entitled "Creating plasma medicine science" in the scientific research fund subsidy project from 2012 to 28. A new academic field has been established and active research has been conducted with the support of the country. At this time, Nagoya University has announced research results such as an increase in the antioxidant content of strawberries grown under low temperature atmospheric pressure plasma irradiation, and a 20% increase in yield. Similarly, at Kyushu University, we have announced results such as promoting the growth of rice by irradiating low-pressure plasma to rice seeds. However, low temperature mutual function of the atmospheric pressure plasma and biological components Section basic research were studied is not sufficiently performed, reality is not yet remarkable progress is seen in the application surface.
This time, National Institutes of Natural Sciences , Nagoya University, and Kyushu University have set up a Plasma Bio Consortium with the aim of developing fusion research between the fields of basic plasma science and life science and making a definite contribution to the industry. In this consortium, we will explore the active application and utilization of "low temperature atmospheric pressure plasma" technology, which is attracting attention as a surface treatment and processing technology in the revolutionary semiconductor manufacturing, to life sciences and medicine, We aim to help expand the base of the Japanese industry.
For example, as typified by water, it is known that a substance changes its state from solid to liquid to gas by raising its temperature. Then, by raising the temperature further from the gas or applying a voltage, ionization occurs, and the substance changes to a state in which neutral molecules, electrons, etc. coexist. This state is called plasma. Auroras and lightning, etc., found in nature are representative of plasma, and technological applications of this are fluorescent lamps and plasma TVs.
Plasma has high particle temperature plasma (high temperature plasma) and low temperature plasma. High-temperature plasma is used in the fusion technology developed by National Institute for Fusion Science, which aims to generate energy equivalent to the sun on the ground. On the other hand, low-temperature plasma has attracted attention in the industrial world due to its versatility, ease of handling, and inexpensive equipment, and is used for semiconductor technology, sterilization and disinfection.
In recent years, research on the application of low-temperature plasma to the fields of life sciences and medicine has been advanced worldwide, and in Japan it is entitled "Creating plasma medicine science" in the scientific research fund subsidy project from 2012 to 28. A new academic field has been established and active research has been conducted with the support of the country. At this time, Nagoya University has announced research results such as an increase in the antioxidant content of strawberries grown under low temperature atmospheric pressure plasma irradiation, and a 20% increase in yield. Similarly, at Kyushu University, we have announced results such as promoting the growth of rice by irradiating low-pressure plasma to rice seeds. However, low temperature mutual function of the atmospheric pressure plasma and biological components Section basic research were studied is not sufficiently performed, reality is not yet remarkable progress is seen in the application surface.
This time, National Institutes of Natural Sciences , Nagoya University, and Kyushu University have set up a Plasma Bio Consortium with the aim of developing fusion research between the fields of basic plasma science and life science and making a definite contribution to the industry. In this consortium, we will explore the active application and utilization of "low temperature atmospheric pressure plasma" technology, which is attracting attention as a surface treatment and processing technology in the revolutionary semiconductor manufacturing, to life sciences and medicine, We aim to help expand the base of the Japanese industry.
Fig. 1 Outline of Plasma Bio Consortium
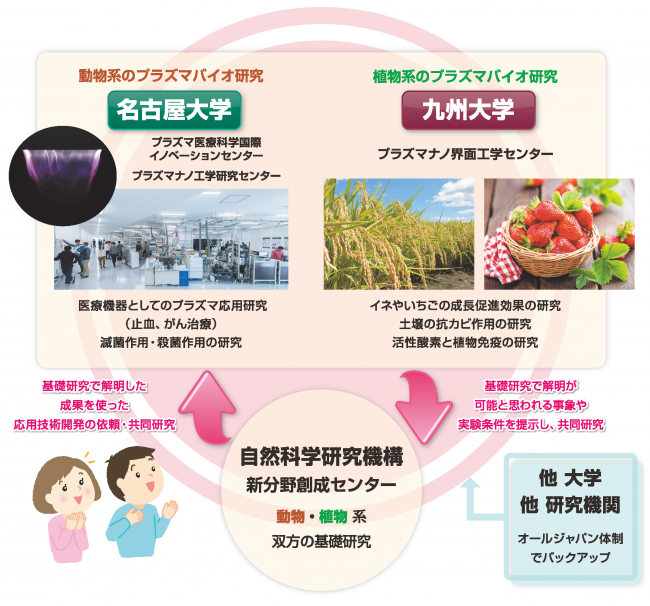
The Plasma Bio Consortium consists of National Institutes of Natural Sciences, Nagoya University and Kyushu University. National Institutes of Natural Sciences mainly conducts basic research on both animal and plant systems at Department of Plasmabio Science, which was newly established at Center for Novel Science Initiatives (CNSI) from this year, and fully supports applied technology development. Nagoya University and Kyushu University have their respective centers for applying plasma technology, and various applied researches have already been developed. In the future, based on the academic support of basic research by National Institutes of Natural Sciences, we will aim for the further development of plasma technology application in the "all Japan system" by joint research with other universities and other research institutes.
Contact
<About research>
National University Corporation Nagoya University
Professor Hori Masaru (Horimasal)
National University Corporation Kyushu University
Professor Shiratani Masaharu (Shiratani Masaharu)
National Institutes of Natural Sciences Center for Novel Science Initiatives (CNSI)
Director Keiji Imoto (Imotokeiji)
<About the Plasma Bio Consortium>
University Joint Research Institute Corporation National Institutes of Natural Sciences
Administrative Bureau Liaison and Planning Division Research Support Section
<Thing about public relations>
Nagoya University General Affairs Department General Affairs Division Public Relations Office
Kyushu University Plasma Nano-Interface Engineering Center
National Institutes of Natural Sciences (NINS)
Assistant Professor Takakazu Sakamoto
National University Corporation Nagoya University
Professor Hori Masaru (Horimasal)
National University Corporation Kyushu University
Professor Shiratani Masaharu (Shiratani Masaharu)
National Institutes of Natural Sciences Center for Novel Science Initiatives (CNSI)
Director Keiji Imoto (Imotokeiji)
<About the Plasma Bio Consortium>
University Joint Research Institute Corporation National Institutes of Natural Sciences
Administrative Bureau Liaison and Planning Division Research Support Section
<Thing about public relations>
Nagoya University General Affairs Department General Affairs Division Public Relations Office
Kyushu University Plasma Nano-Interface Engineering Center
National Institutes of Natural Sciences (NINS)
Assistant Professor Takakazu Sakamoto
Release source
Plasma bioconsortium
Inter-university Research Institute Corporation Natural Science Research Machine
Nagoya University
Kyushu University
Inter-university Research Institute Corporation Natural Science Research Machine
Nagoya University
Kyushu University





